Arrae Health: Primary Care Physician | Senior Health Services in Corona & Palm Springs
23 Oct, 2024
Optimizing PAD Care for the Elderly: Treatment Strategies from Arrae Health
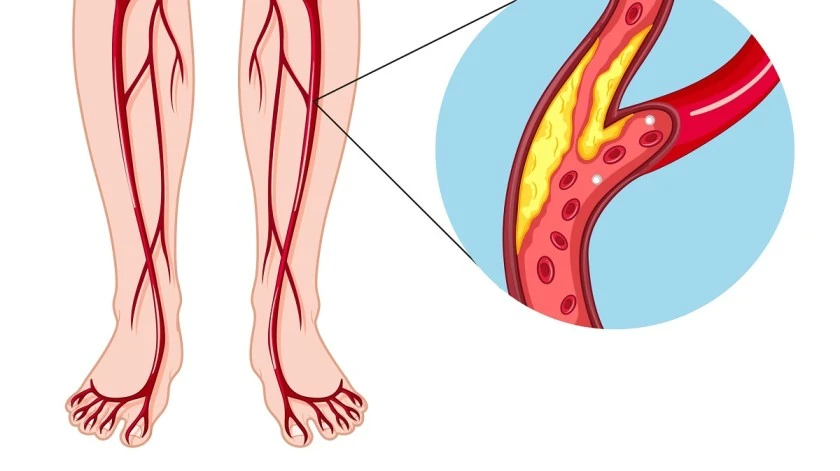
Peripheral artery disease (PAD) is a common yet often overlooked condition, especially among the elderly. It affects blood vessels outside the heart and brain, most commonly in the legs, and can lead to pain, numbness, and difficulty walking, significantly impacting quality of life. Fortunately, PAD can be managed effectively with the right strategies and care.
At Arrae Health Corona & palm Spring, we focus on optimizing PAD care for older adults, ensuring better health and improving quality of life. Your trusted partner for comprehensive PVD treatment & PAD care. We offer advanced therapies to improve blood flow and enhance your quality of life.
Understanding PAD and Its Impact
PAD is characterized by the narrowing of lower extremity arteries due to plaque build-up, which slows blood flow and leads to symptoms such as:
- Intermittent Claudication: Pain or cramping in the legs during activity, which improves with rest.
- Rest Pain: Persistent pain in the legs even while at rest, which may indicate critical PAD.
- Non-Healing Wounds: Sores on the feet or legs that fail to heal properly.
- Numbness or Weakness: Loss of feeling or strength in the legs, which can be particularly challenging for older individuals.
Comprehensive Assessment and Diagnosis
A thorough assessment and diagnosis are crucial for optimizing PAD care. This typically involves:
- Review of Medical History: Evaluating the patient’s overall health, previous conditions, and lifestyle.
- Physical Examination: Checking for PAD symptoms, such as skin discoloration and diminished lower extremity pulses.
Accurate diagnosis allows health practitioners to tailor Treatment of PAD in elderly strategies to the specific needs of elderly patients with PAD.
Lifestyle Modifications
Managing PAD and improving overall health often require lifestyle changes, including:
- Smoking Cessation: Smoking is a major cause of PAD. Quitting smoking helps alleviate symptoms and slow disease progression.
- Healthy Diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean meats can help control cholesterol and blood pressure, both crucial for managing PAD.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in exercise promotes blood flow and reduces pain from walking or movement. While walking is often recommended, the best type of exercise depends on individual capabilities.
Medication Management
Medications play a vital role in treating PAD and preventing complications. Commonly prescribed drugs include:
- Antiplatelet Agents: Aspirin or clopidogrel help prevent blood clots and reduce the risk of heart attacks or strokes.
- Statins: These medications lower cholesterol levels and slow PAD progression.
- Pain Relievers: Drugs like cilostazol may reduce pain associated with exercise.
Regular follow-ups with a healthcare provider are essential to assess the effectiveness of medications and make any necessary adjustments.
Wound Care and Foot Health
Good foot and wound care are critical for older individuals with PAD to prevent infections and non-healing sores. Key practices include:
- Daily Foot Inspection: Regularly check your feet for cuts or blisters, and consult a doctor if any issues are detected.
- Proper Footwear: Wear comfortable, supportive shoes to prevent foot injuries.
- Wound Care: Properly care for ulcers or sores by keeping wounds clean, applying appropriate dressings, and seeking medical advice when needed.
Managing Comorbid Conditions
Many older adults with PAD also have comorbid conditions, such as diabetes, hypertension, or heart disease. Effective management of these conditions is crucial for overall health and PAD management. This may involve:
- Diabetes Management: Controlling blood sugar levels to prevent complications and improve PAD symptoms.
- Blood Pressure Control: Managing blood pressure through lifestyle changes and medications to reduce cardiovascular risks.
- Cardiovascular Health: Monitoring and treating heart disease to improve circulation and alleviate PAD symptoms.
Patient Education and Support
Education about PAD and its management is essential. At Arrae Health, we emphasize:
- Understand the Disease: Learning about PAD, its symptoms, and management strategies.
- Self-Care Techniques: Teaching patients how to manage their condition, including understanding their medications, and practicing proper foot care.
- Support Systems: Encouraging the use of support groups and counseling services to help patients cope with the emotional and mental challenges of living with PAD.
Collaborative Care
Effective PAD management often requires a team approach, involving:
- Primary Care Physicians: Overseeing general health and coordinating care.
- Specialists: Cardiologists or vascular surgeons for advanced PAD stages.
- Registered Dietitians and Exercise Specialists: Providing personalized nutrition and exercise guidance.
- Podiatrists: Offering specialized foot care and wound management.
A multidisciplinary approach, including lifestyle modifications, medication management, wound care, and a collaborative care team, can significantly improve health outcomes and quality of life for elderly individuals with PAD. For assistance or questions about PAD management, please contact Arrae Health. We Also provide Vitamin B12 Injections service at Arrae Health.
FAQs:
Q. What are the early signs and symptoms of PAD in older people?
Ans: Common early signs of PAD include leg pain or cramping during walking or exercise, numbness or tingling in the feet, and slow-healing sores or ulcers.
Q. How can I prevent the progression of PAD?
Ans: Preventing PAD progression involves adopting a healthy lifestyle, including balanced nutrition, regular exercise, smoking cessation, and weight management.
Q. What are the available treatment options for PAD in the elderly?
Ans: Treatment of PAD in elderly may include lifestyle modifications, medications, interventional procedures, and wound care. The most suitable option depends on the severity of the condition and the patient’s overall health.
